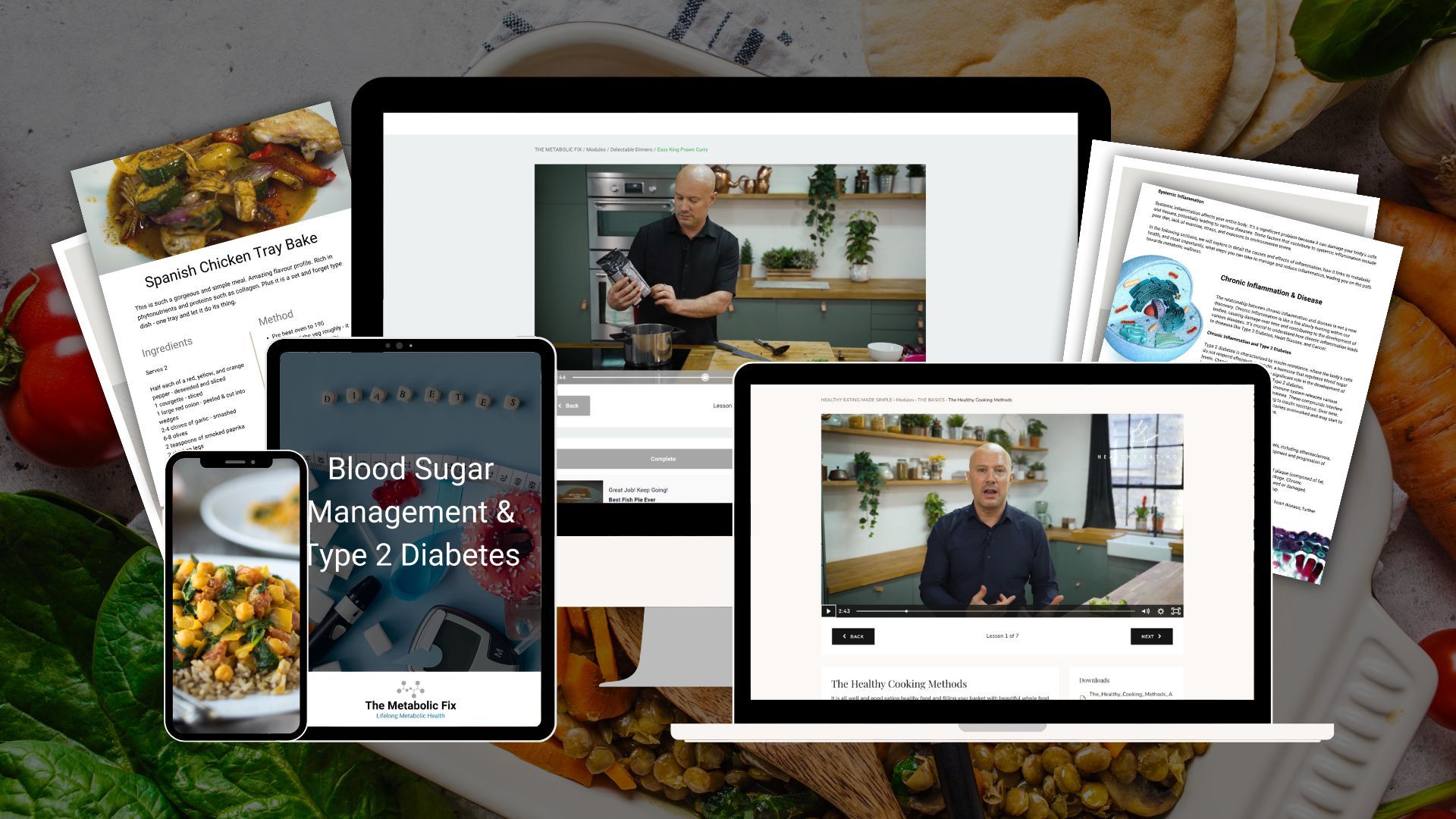
Omega 3 & Blood Pressure
Dec 30, 2023
Imagine a nutrient so powerful that it can subtly influence the rhythm of your heart and the pulse of your blood vessels. Omega-3 fatty acids are just that - unsung heroes in the world of heart health. Long term followers of my work know that I am a tad obsessed with them because of the vast positive impacts they have upon our health, Here, we dive deep into how these essential fats sway the tides of our blood pressure.
What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Just in case you are new to this site. Omega-3s are a group of fats that our bodies can't make but desperately need. You've got ALA, a plant-based omega 3 that, in my opinion is a very very poor option for Humans, EPA and DHA, the marine dynamos. Each plays its unique part in keeping us healthy (Swanson et al., 2012).
The Heart of the Matter: Omega-3 and Blood Pressure
Gleaning Insights from Studies
The dance between omega-3 and blood pressure isn't anything new. A meta-analysis, by Miller et al. (2014) showed that fish oil, brimming with EPA and DHA, gently lowers blood pressure, especially in those with hypertension.
Behind the Scenes
Why do omega-3s work their magic on blood pressure? The answer lies in a maze of biological pathways. They improve how blood vessels function, dial down inflammation, and help regulate heart rate and pressure (Kris-Etherton et al., 2002).
From Labs to Life
Real people, real results. In a clinical trial, Mori et al. (1999) showed that fish oil supplements, when taken daily, can significantly calm down both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in those with hypertension. This seems to be dose dependent, and an intake of around 750mg of EPA and 250mg DHA was in the optimal zone.
Sourcing Omega-3: A Practical Guide
To reel in these benefits, the American Heart Association suggests two servings of fatty fish per week. Not a fish fan? ALA-rich foods or supplements can offer SOME degree of benefit, but the conversion in the body to EPA and DHA is nowhere near as good (Kris-Etherton et al., 2002).
Beyond Blood Pressure
Omega-3s are not one-trick ponies. They're known to slash triglyceride levels, keep heart rhythms steady, and slow the buildup of arterial plaques (Mozaffarian & Wu, 2011).
In a nutshell, omega-3s could be a key player in the game of blood pressure management. Embracing a diet rich in these fats might just be what your heart needs. But, as always, tread the path with guidance from health professionals.
References
- Kris-Etherton, P.M., Harris, W.S., Appel, L.J., et al. (2002). 'Fish Consumption, Fish Oil, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, and Cardiovascular Disease.' Circulation, 106(21), 2747-2757.
- Miller, P.E., Van Elswyk, M., Alexander, D.D. (2014). 'Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.' American Journal of Hypertension, 27(7), 885-896.
- Mori, T.A., Burke, V., Puddey, I.B., et al. (1999). 'Purified eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids have differential effects on serum lipids and lipoproteins, LDL particle size, glucose, and insulin in mildly hypertensive subjects.' American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 71(5), 1085-1094.
- Mozaffarian, D., Wu, J.H. (2011). 'Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease: Effects on Risk Factors, Molecular Pathways, and Clinical Events.' Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 58(20), 2047-2067.